Runtime Mechanism
Mini-Program Runtime Mechanism
1. Mini-Program Lifecycle
A mini-program goes through various states from startup to termination, each exhibiting different behaviors.
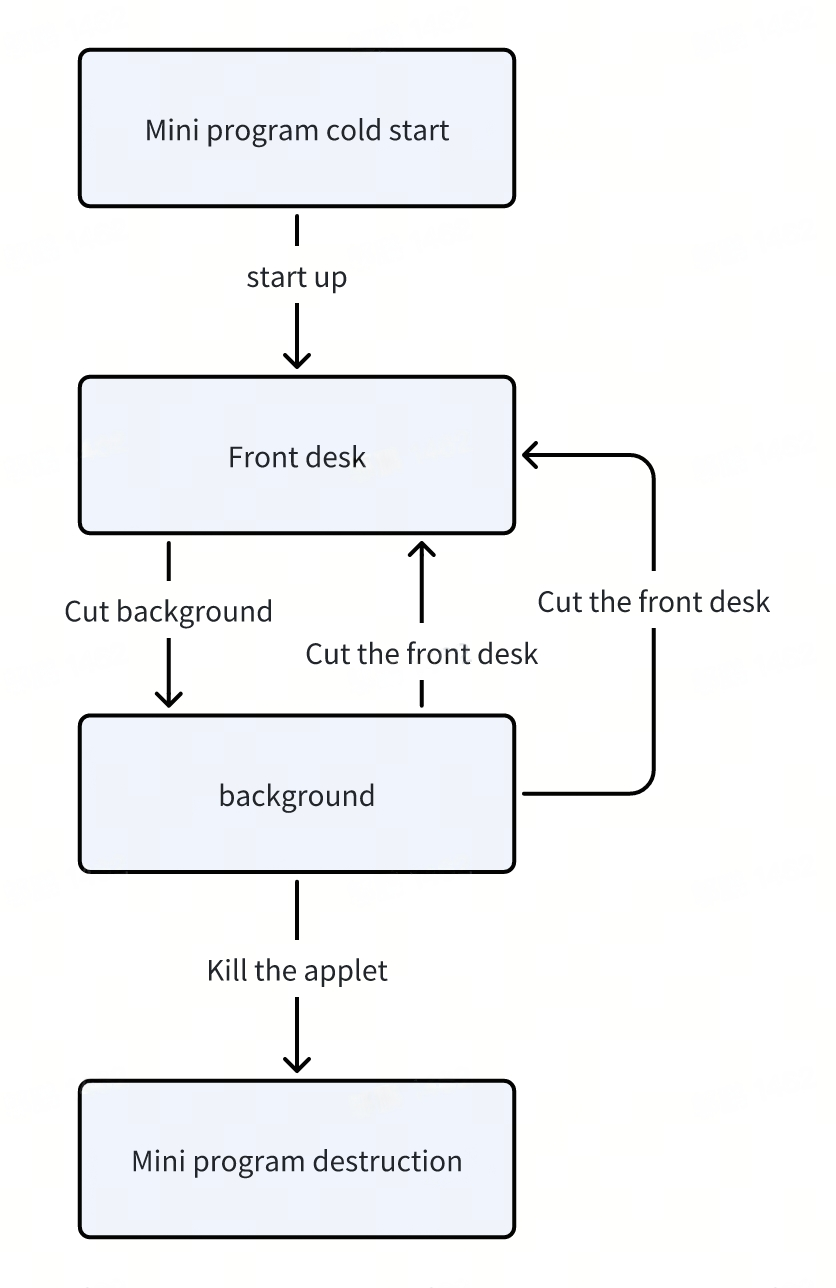
1.1 Mini-Program Startup
From the user's perspective, the startup of a mini-program can be broadly categorized into two scenarios: cold startup and warm startup.
Cold Startup: If a user opens the mini-program for the first time or reopens it after being terminated, the mini-program needs to reload and start from scratch, which is called a cold startup.
Warm Startup: If a user has already opened a mini-program and then reopens it within a certain period, the mini-program is not terminated but instead transitions from the background to the foreground, which is known as a warm startup. From the perspective of the mini-program lifecycle, the term "startup" typically refers to a cold startup, while a warm startup is often referred to as switching from the background to the foreground.
1.2 Foreground and Background
Once a mini-program is launched, its interface is presented to the user, putting it in the foreground state.
When a user "closes" the mini-program, it doesn't actually terminate but instead enters the background state. In this state, the mini-program can continue running for a short period, although some APIs may be restricted. Ways to transition to the background include, but are not limited to:
- Tapping the capsule button in the upper right corner to exit the mini-program.
- Directly switching to the background while the mini-program is running in the foreground (via gestures or the home button).
- Directly locking the screen while the mini-program is running in the foreground.
When the user reopens the mini-program, it returns to the foreground state.
1.3 Mini-Program Termination
A mini-program may be terminated either by the user actively killing the process or by the system due to excessive resource consumption.
2. Pages on Cold Startup
During a cold startup of a mini-program, the following scenarios occur:
- If no path is provided in the startup scene, the program enters the home page.
- If a path is provided in the startup scene, the program navigates to the corresponding page.
3. Pages on Warm Startup
During a warm startup of a mini-program, the following scenarios occur:
- If no path is provided in the startup scene, the program retains the previous browsing state.
- If a path is provided in the startup scene, the program relaunches to the corresponding page.